According to a recent article in The Wall Street Journal, “Cognitive problems are among the most persistent and common lasting effects of COVID.” Many of these cognitive issues are becoming long-term symptoms months after an active COVID dx.
It’s important that we understand Post-COVID-19 syndrome, which is signs and symptoms that develop during or after an infection consistent with COVID-19, continue for more than 12 weeks, and are not explained by an alternative diagnosis. Post-COVID-19 syndrome may be considered before 12 weeks while the possibility of an alternative underlying disease is also being assessed. These patients are also commonly referred to as “long-haulers.”
Therapy teams need to take an active role in the ongoing assessment and intervention of cognition. It’s especially important to know the patient’s PLOF and not discontinue services too soon, knowing that cognitive impairments with this population will continue long after the active diagnosis. Cognitive intervention is also important for our outpatient population in both ALFs and in the community. Physicians need to know that we are available to partner with post-COVID patients who have lingering cognitive issues.
Starting with a brief assessment such as the St. Louis University Mental Status Exam (SLUMS); Clock Drawing Test; Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Exam (ACE); or MINI-COG will provide initial information on the level of cognitive impairment (none, mild, Dementia level).
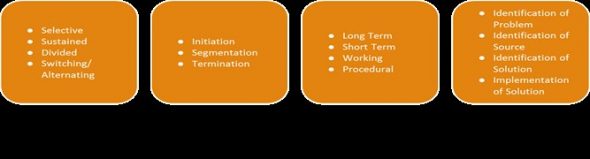
Once determined, it is clinically recommended to complete a formal standardized assessment and log Cognitive Performance Assessment 96125. Examples include: Ross Information Processing Assessment-Geriatric Edition (RIPA-G); Cognitive Linguistic Quick Test (CLQT); Functional Linguistic Communication Inventory (FLCI); The Scales of Cognitive and Communicative Ability for Neurorehabilitation (SCCAN); and Functional Assessment of Verbal Reasoning and Executive Strategies (FAVRES). Utilize assessments that at minimum can address: memory (i.e., list learning task; paragraph recall task; digit repetition, etc.); working memory/executive function; executive function (problem solving; planning; inhibition/initiation); and processing speed.
Once the assessments are completed, clinicians will know which areas of cognition to target with skilled intervention. Please refer to the various POSTettes (Post COVID; Cognitive Performance Assessment; SLP Cognitive Impairments) and the Cognitive Impairments Clinical Guide for additional information.
By Tamala Sammons, M.A., CCC-SLP, Therapy Resource